1.8 Exercises
NCERT Class 9 Science Textbook for Blind and Visually Impaired Students made Screen Readable by Professor T K Bansal.
Q1. Convert the following temperatures to the Celsius scale.
(a) 300 K
(b) 573 K.
A1.
(a) = 300 -273 = 27 ° C;
(b) = 573 -273 = 300° C.
Q2. Convert the following temperatures to the Kelvin scale.
(a) 25°C
(b) 373°C
A2.
(a) = 298 K
(b) = 646 K
Q3. Give reason for the following observations.
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
(b) We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
A3.
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid due to sublimation.
(b) Particles of the aroma of perfume mix with air and consequently move with it, which is why we are able to get the smell of the perfume. This phenomenon is known as diffusion.
Q4. Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles- water, sugar, oxygen.
A4. Oxygen, water and sugar
Q5. What is the physical state of water at each of the following temperatures?
(a) 25°C,
(b) 0°C, and
(c) 100°C ?
A5.
(a) Liquid,
(b) Freezing
(c) Boiling.
Q6. Give two reasons to justify-
(a) water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
A6
(a) The intermolecular forces in water are not as strong. The water molecules are held to each other by weak forces known as hydrogen force.
(b) The atoms of iron are held to each other by strong metallic bond, that is why the iron is a solid at room temperature.
Q7. Why is ice at 273 K more effective for cooling than water at the same temperature?
A7. Ice at 273K has to melt so as to cool its surroundings, and possesses a large value of latent heat. Whereas, water at 273K is already in liquid state.
Q8. What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
A8. Steam causes more severe burns as compared to water, due to its large value of latent heat.
Q9. Name A,B,C,D,E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state
Diagram. 10A
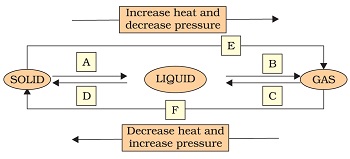
“Image description by Dr T K Bansal begins; This figure is in the form of a flow diagram. At the top there is a arrow from left to right on which it is written that increase heat and decrese pressure.Below it there is another arrow from right to left on which it is mentioned that decrease heat and increase pressure. Between these two arrows three boxes are made in which solid, liquid and gas are written from left to right and these three are connected to each other with arrows. These arrows are marked with letters like a, b, etc. Arrow from solid to liquid is marked as ‘A’, Arrow from liquid to gas is marked as ‘B’. Arrow from gas to liquid is marked as ‘C’, Arrow from liquid to solid is marked as ‘D’, Arrow from solid to gas is marked as ‘E’, Arrow from gas to solid is marked ‘F’. Image description ends.”
A9.
(a) Melting,
(b) Boiling,
(c) Condensation,
(d) Freezing,
(e) Sublimation, and
(f) Sublimation.
